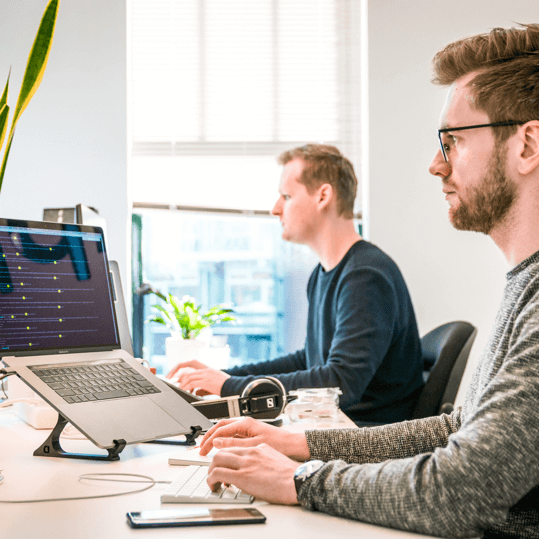
Go Beyond Your Wildest Dreams
Your Digital Presence Is About To Take Off
We build empires, break barriers, and turn clicks into loyal customers.
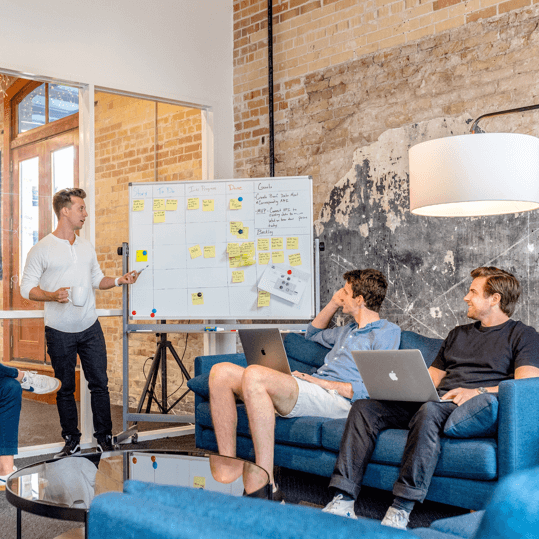
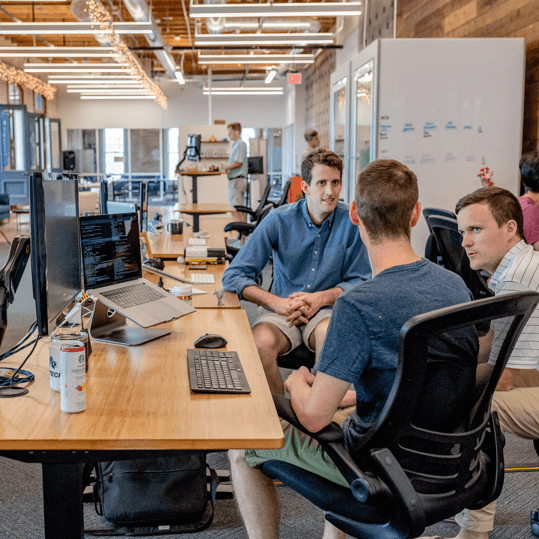


The Sky's The Limit
We Create Unique Campaigns That Help Your Business Grow
We Solve Real Problems
what can we do for you?
Social Media
We’re proud to be the social media engine for brands that dare to stand out and lead conversations.

SEO
We help businesses grow by making sure they’re easy to find online. With smart SEO strategies, we boost your website’s ranking, drive real traffic, and turn visitors into customers.

PPC
We create high-impact PPC campaigns that bring you the right traffic fast. From Google Ads to social media, we make every click count — boosting your leads, sales, and growth without wasting your budget.
Strategy
We design beautiful, user-friendly websites that not only look great but also work hard to turn visitors into customers.

Web Design
We build custom content plans that align with your goals — making sure every post, blog, and campaign works together to grow your business and boost your brand voice.

Content Marketing
We create powerful content that speaks to your audience, builds trust, and drives real action.
Timothy Powell
Lisa R. Boone
our work inspires smiles
The Faces Behind Our Success
Meet Our Clients
They Believe In Us
we are proud to partner with some of the most innovative and inspiring brands across a wide range of industries.
Our clients trust us to deliver exceptional quality, personalized service, and results that drive real success.






Do You Want To Boost Your Business?
drop us a line and keep in touch
